
152 High Rd, Byfleet, Surrey, KT14 7RG / 01932 341415 / surreyperio@gmail.com
Receding gums, also known as gingival recessions, refer to the gradual exposure of the tooth’s root due to the loss of gum tissue. This common dental condition can lead to increased tooth sensitivity, an aged appearance, and, if left untreated, potential oral health complications. Understanding the causes and treatments for receding gums are essential for maintaining optimal oral well-being.
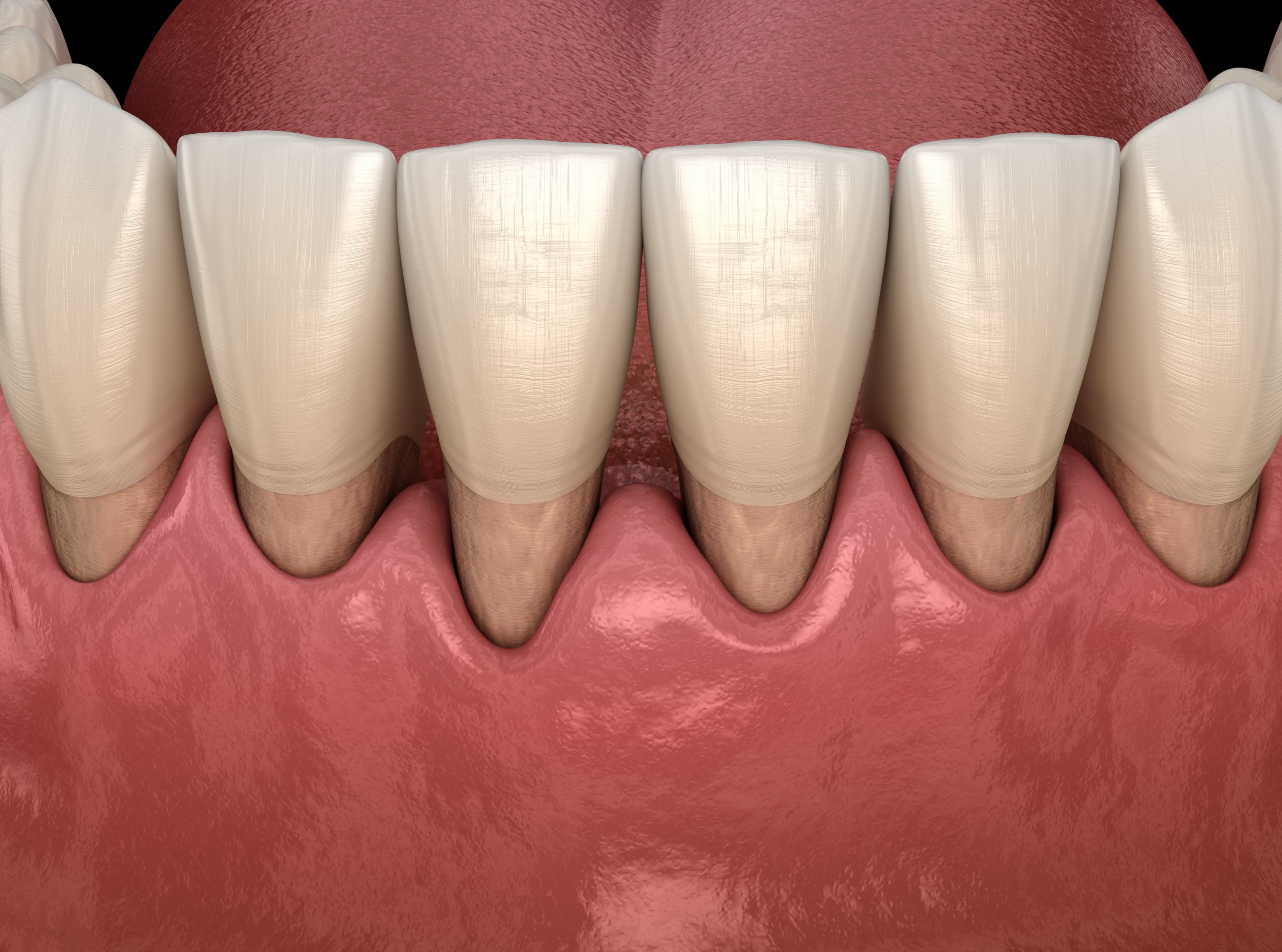
Several factors contribute to the development of receding gums, including:
Preventing and treating gum recessions involves maintaining good oral hygiene practices, including regular brushing, flossing, and professional dental cleanings. Addressing contributing factors like teeth grinding may involve the use of mouthguards. In more advanced cases, a periodontist (a specialist in the treatment of gum-related issues) may recommend procedures such as gum grafting. This involves taking tissue from another part of the mouth or using donor tissue to cover exposed tooth roots, helping to reduce sensitivity and improve the appearance of the gums.
Treatment for receding gums depends on the severity of the condition. Common approaches include:
Treatment starts by addressing the problem which caused the gum recession i.e. treating gum infection, correcting tooth position, correcting wrong brushing techniques etc.
Gum recessions are then treated by repositioning the gums (“Pulling the gums up”) and/or by doing gum grafts. Gum grafts are done with your own tissue (taking gum from the roof of your mouth) or by using a gum substitute like AlloDerm®.
Treatment can reduce further recession & bone loss, cover exposed tooth roots (to protect them from decay), reduce tooth sensitivity and improves the appearance of your smile.
Whether you have treatment to improve function or aesthetics, you often receive the benefits of both: improved periodontal health and an improved smile. Both are key to smiling, eating and speaking with comfort and confidence.

Yes, in many cases receding gums can be fixed. Once the gum disease has been treated, we are able to perform a gum graft. Please note that some gum recessions are only “fixed” by using restorations like white fillings, crowns, or veneers.
If you suspect you have receding gums or just want to check on your gum health, the best first step is to book an appointment with your dentist/hygienist or with a specialist periodontist who will be able to advise further.
In short, receding gums cannot be “pushed back”. Nor will they grow back naturally. Gum recessions are mostly treated with a gum grafts. This involves removing a bit of gum from the roof of your mouth and transplanting it to the receding area.
While age doesn’t cause gums to recede, it does tend to become more common as we get older.
Studies show that between the ages of 30-39, about 40 % of us will have some gum recessions. This incidence will keep increasing with around 70% of individuals having some form of receding gums by ages 50-59, and 90% between ages 80-89.
Stopping the progression of receding gums depends on the cause of onset. You will need to arrange a consultation with a periodontist, and they will be able to assess the cause and advise treatment going forward.
If you’re worried about your gum recessions, book a consultation with us today.